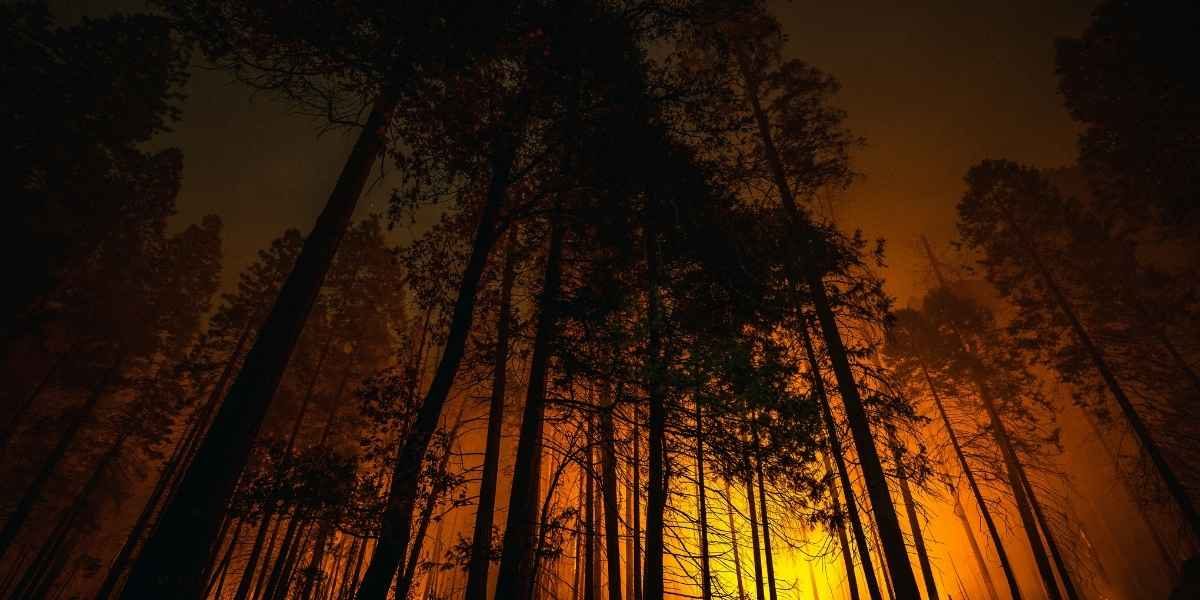
Wildfires in the United States are becoming more frequent and severe, posing a significant threat to communities, ecosystems, and the economy. While natural causes such as lightning have always played a role, human activities and climate change are accelerating the frequency and intensity of these events. To address this growing crisis, it is crucial to understand the causes, consequences, and potential strategies for mitigating the devastating impacts of wildfires.
Read Also: How Extreme Weather Conditions Are Impacting US Agriculture
What Causes Wildfires in the USA?
Wildfires can originate from both natural and human-induced factors. Lightning strikes have historically been one of the primary natural causes, igniting fires in dry, forested regions. However, human activities now account for the majority of wildfires in the United States. Unattended campfires, discarded cigarettes, equipment sparks, and intentional arson significantly contribute to fire incidents across the country.
Climate change has exacerbated the conditions that allow wildfires to thrive. Rising temperatures and prolonged droughts are drying out vegetation, creating vast expanses of easily ignitable fuel. Strong winds, particularly in regions like California, can rapidly spread flames, making containment efforts more challenging. Urban expansion into fire-prone areas further increases the risk of ignition, putting more lives and properties at stake.
The complexity of wildfire causes highlights the importance of adopting a multifaceted approach to prevention. Understanding these factors helps in crafting targeted solutions to reduce the likelihood of ignition and the scale of destruction.
How Do Wildfires Impact Communities and Ecosystems?
The consequences of wildfires are far-reaching and often catastrophic. Communities in wildfire-prone areas face immediate threats to life and property. Flames can engulf entire neighborhoods within hours, leaving residents with little time to evacuate. Beyond the physical destruction, wildfire survivors often experience long-term emotional and financial stress, as rebuilding efforts take years and are accompanied by significant costs.
The environmental impacts are equally severe. Wildfires destroy vast swaths of forests, leading to habitat loss for countless species. The destruction of vegetation contributes to soil erosion, while the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere exacerbates global warming. Water quality also suffers, as ash and debris contaminate rivers and reservoirs. The loss of trees and other vegetation can disrupt local ecosystems, leading to imbalances that may take decades to recover.
On a broader scale, wildfires have a profound economic impact. In addition to the costs of firefighting and recovery efforts, businesses and industries dependent on natural resources, such as agriculture and tourism, suffer significant losses. The ripple effects of these disruptions often extend far beyond the immediate vicinity of the fire, affecting regional and even national economies.
What Strategies Can Help Mitigate the Impact of Wildfires?
Mitigating the impact of wildfires requires a combination of preventive measures, community preparedness, and effective response strategies. One of the most effective ways to prevent wildfires is through public awareness campaigns. Educating residents about fire safety practices, such as properly extinguishing campfires and avoiding risky behaviors during high-risk periods, can significantly reduce human-caused ignitions.
Forest management practices also play a crucial role. Controlled burns, also known as prescribed fires, help reduce the buildup of dry vegetation that fuels larger wildfires. Thinning forests and creating defensible spaces around homes and infrastructure can limit the spread of flames. Advances in technology, such as satellite monitoring and predictive modeling, provide early warnings and help allocate firefighting resources more efficiently.
Community preparedness is another critical aspect. Evacuation plans should be regularly updated and communicated to residents in high-risk areas. Building codes can be adjusted to require fire-resistant materials for homes and other structures. Investing in infrastructure, such as firebreaks and water storage facilities, can further enhance a community’s resilience to wildfires.
On a policy level, addressing climate change is essential to reducing the long-term risk of wildfires. Policies that promote renewable energy, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and enhance environmental conservation efforts can mitigate the conditions that contribute to wildfire severity. Collaboration between federal, state, and local governments ensures that resources are effectively deployed where they are needed most.
Why Raising Awareness and Taking Action Matters
Wildfires are no longer isolated incidents; they are a growing crisis with widespread consequences. The rising frequency and intensity of these events underscore the urgent need for comprehensive solutions. Public awareness, proactive measures, and policy changes are key to mitigating their devastating effects.
By understanding the factors that contribute to wildfires and the consequences they bring, individuals and communities can take informed action. Simple steps, such as adhering to fire safety guidelines, supporting conservation efforts, and advocating for climate policies, can collectively make a significant difference. Every effort counts in reducing the risk and impact of wildfires.
Read Also: How to Use Credit Cards to Build Financial Health
The fight against wildfires is not just about prevention but also about building resilience. While it may not be possible to eliminate wildfires entirely, mitigating their effects can save lives, protect ecosystems, and preserve economic stability. As the United States faces an increasingly volatile fire landscape, collaboration, innovation, and determination will be essential to overcoming this challenge.