The Northern Hemisphere: Geography, Climate, and Human Impact
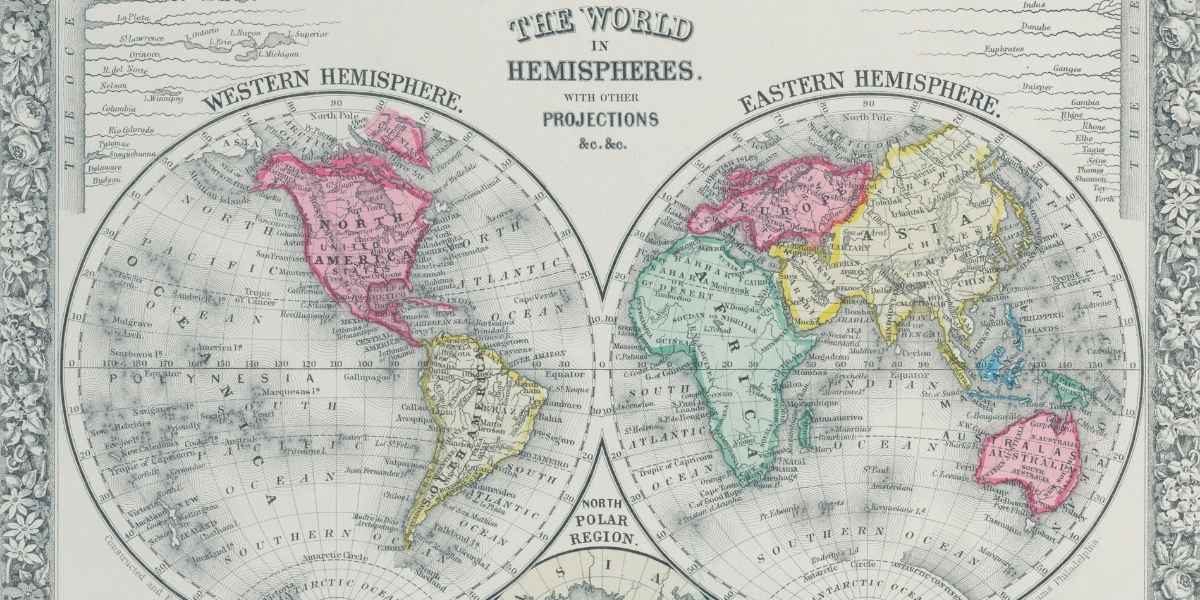
The Northern Hemisphere, which comprises about 90% of Earth’s human population, is home to a diverse range of geographical features, climates, and ecosystems. From vast mountain ranges to dense forests and sprawling deserts, the region offers a unique tapestry of natural wonders. But it’s not just the natural environment that defines this part of the world—human activities, both ancient and modern, have significantly shaped its landscapes and climate. Understanding the geographical, climatic, and human influences in the Northern Hemisphere provides valuable insights into how we coexist with our planet and its resources.
Read Also: The Longest Day: Exploring the Summer Solstice
What Defines the Geography of the Northern Hemisphere?
Geographically, the Northern Hemisphere includes much of the Earth’s landmass, consisting of Asia, Europe, North America, and parts of Africa and Oceania. Major physical features such as the Himalayas, Rocky Mountains, and Alps dominate the landscape, while vast plains and valleys like the Great Plains of North America and the Russian Steppes add diversity to the terrain. Additionally, the Northern Hemisphere is home to the world’s largest oceans—the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans—which influence much of the climate and weather patterns in the region.
In this hemisphere, the Equator runs through the middle, dividing it into the tropical, temperate, and polar zones. The diverse range of landscapes in the Northern Hemisphere supports a variety of ecosystems, from the taiga in northern Canada to the savannas in parts of Africa. This variety creates a rich biodiversity, which is essential for understanding both the region’s ecosystems and human adaptation to these environments.
How Does the Climate Vary Across the Northern Hemisphere?
The climate of the Northern Hemisphere is shaped by its vast size and varied geographical features. As the region spans from the Arctic Circle to the tropics, its climates are just as diverse. In the northernmost areas, polar climates dominate, characterized by freezing temperatures and long winters, as seen in parts of Alaska and Northern Canada. These areas are home to few people, but the ecosystems are home to unique species like polar bears and arctic foxes.
Further south, the temperate climates are more common, with distinct seasons and moderate temperatures. Countries like the United States, China, and much of Europe fall into this climate zone, offering favorable conditions for agriculture, urbanization, and human settlement. In these regions, cities like New York, London, and Paris thrive thanks to mild winters and warm summers.
Tropical climates are found closer to the Equator, where countries like India, Brazil, and Central Africa experience hot, humid weather year-round. These regions support lush rainforests, savannas, and diverse wildlife. The variations in climate significantly affect agricultural practices, food production, and human lifestyles across the Northern Hemisphere, making it a region rich in resources but also vulnerable to climate change.
What Impact Have Humans Had on the Northern Hemisphere’s Geography?
Human activity has drastically altered the landscape of the Northern Hemisphere. Over the centuries, civilizations have cleared forests, constructed cities, and developed infrastructures such as roads, dams, and railways. The industrial revolution, which began in Europe and North America, accelerated these changes, contributing to urbanization, deforestation, and the transformation of natural environments into agricultural land.
Agriculture has had a major impact on the geography of the Northern Hemisphere. Large-scale farming, particularly in the United States, China, and Russia, has altered ecosystems, displaced native species, and contributed to soil degradation in some areas. Irrigation projects in arid regions, such as in parts of North Africa and the Middle East, have transformed deserts into agricultural hubs, providing food and resources to millions.
The urbanization of major cities, such as New York, Tokyo, and Moscow, has led to the replacement of natural landscapes with concrete, buildings, and infrastructure. These cities have become the economic and cultural centers of their respective countries, yet they also contribute to air pollution, waste generation, and the alteration of local climates, particularly through the urban heat island effect.
How Is Climate Change Affecting the Northern Hemisphere?
Climate change is having a profound effect on the Northern Hemisphere. Rising global temperatures are contributing to the melting of polar ice caps in regions like the Arctic, threatening both ecosystems and coastal communities. As the ice melts, it exposes darker ocean surfaces, which absorb more heat, exacerbating the warming cycle. This is leading to the rise in sea levels that could flood low-lying coastal cities.
In addition to rising temperatures, extreme weather events are becoming more frequent. Heatwaves, droughts, and floods have already impacted areas in the United States, Southern Europe, and China. These changes threaten agriculture, leading to crop failures in some regions while benefiting others. For example, warmer winters in northern regions like Russia could allow for longer growing seasons, but the overall negative effects outweigh the positives.
The tropical regions are also feeling the effects of climate change, with rising sea levels threatening low-lying islands in the Caribbean and Pacific Ocean. Changes in rainfall patterns are intensifying the severity of hurricanes and monsoons, which are becoming more destructive as the climate warms. Overall, human-induced climate change is drastically altering both the climate and geography of the Northern Hemisphere, putting strain on ecosystems, agriculture, and human populations.
What Steps Can Be Taken to Mitigate Human Impact on the Northern Hemisphere?
While the Northern Hemisphere faces numerous challenges due to human activity and climate change, there are steps that can be taken to mitigate further damage. Sustainable development practices, such as promoting renewable energy, reducing carbon emissions, and implementing green technologies, are crucial in curbing the negative impacts on the environment. Cities around the world are beginning to incorporate green spaces, renewable energy sources, and energy-efficient buildings to reduce their environmental footprint.
Read Also: North Pole: The Frozen Frontier
On a larger scale, international cooperation is necessary to address the issue of climate change. Agreements such as the Paris Climate Agreement aim to limit global temperature rise by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Efforts to protect biodiversity through conservation projects and the establishment of protected areas also play a vital role in preserving the Northern Hemisphere’s ecosystems.
Individuals can also contribute by adopting more sustainable lifestyles, such as reducing waste, supporting sustainable agriculture, and conserving water. By combining efforts at the individual, national, and global levels, humanity can help mitigate the human impact on the Northern Hemisphere’s geography and climate.