As concerns about food security, sustainability, and healthy living grow, urban farming has become a major trend across the United States. Urban farms and community gardens are popping up in cities large and small, turning rooftops, vacant lots, and even warehouses into spaces for growing fresh, local produce. Here’s how urban farming is transforming American cities and why it matters for our communities, economy, and environment.
The Rise of Urban Farming in the U.S.
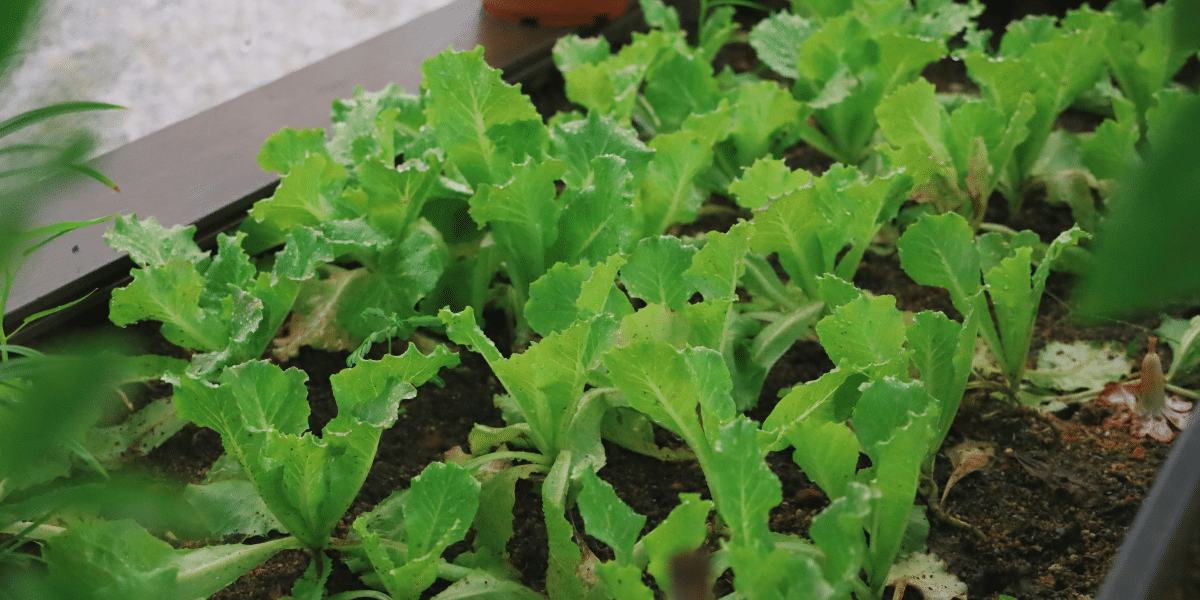
Urban farming is the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. While farming is traditionally associated with rural areas, city dwellers are increasingly embracing the idea of growing food close to home. The COVID-19 pandemic heightened awareness around food supply chains and access to fresh produce, sparking an interest in urban farming and self-sustainability.
In cities like New York, Los Angeles, and Chicago, urban farms are taking root on rooftops, in vacant lots, and even on vertical walls. Some urban farms are run by individual enthusiasts or small communities, while others are large-scale commercial ventures aimed at supplying fresh food to local grocery stores and restaurants. This growing movement is helping cities reduce food deserts, promote local food economies, and improve access to healthy foods.
Environmental Benefits of Urban Farming
Urban farming offers a range of environmental benefits that make it appealing for cities looking to reduce their carbon footprint. By producing food locally, urban farms cut down on the distance food travels from farm to table, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Transportation, packaging, and storage associated with conventional farming all contribute to carbon emissions, but urban farming minimizes these environmental costs.
Additionally, urban farms can help combat the “heat island effect” in cities, where dense urban areas become significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas due to human activity and infrastructure. Green rooftops and community gardens cool the environment, absorb rainwater, and reduce air pollution. Urban farming also promotes biodiversity in city ecosystems, attracting pollinators like bees and butterflies that are essential for healthy food production.
Addressing Food Insecurity in Urban Areas
Food insecurity is a pressing issue in many American cities, with millions of people lacking reliable access to affordable, nutritious food. Urban farming has emerged as a powerful tool for addressing food deserts, areas where fresh produce is scarce. By growing food locally, urban farms can bring fresh fruits and vegetables directly into communities that need them most.
Non-profit organizations and community groups are increasingly investing in urban farming initiatives to address food insecurity. Programs like the Detroit Black Community Food Security Network are working to create local food systems that are affordable and accessible. In New York City, the organization GreenThumb supports over 550 community gardens, providing fresh produce and educational resources to neighborhoods throughout the city. These projects not only provide food but also empower residents to take control of their food sources and build community resilience.
Innovative Approaches to Urban Farming
Urban farming is evolving with new techniques that maximize space and productivity. Hydroponics, for example, is a soil-free method of growing plants that uses nutrient-rich water, allowing crops to be grown vertically and indoors. Companies like Bowery Farming and Gotham Greens use hydroponics to produce leafy greens in indoor, climate-controlled environments, supplying fresh produce to urban markets year-round.
Another innovative approach is aquaponics, which combines fish farming with plant cultivation in a closed-loop system. The waste from the fish provides nutrients for the plants, while the plants filter and clean the water for the fish. Aquaponics systems are popular in urban farming because they are efficient, sustainable, and can be set up in small spaces, making them ideal for densely populated areas.
Vertical farming is also gaining traction in cities with limited land space. Vertical farms grow crops in stacked layers, usually in indoor environments, maximizing yield in a small footprint. Companies like AeroFarms use vertical farming to produce greens and herbs, leveraging LED lights and climate control to create optimal growing conditions. These innovative approaches are making it possible to produce more food in smaller urban spaces, meeting the needs of growing city populations.
Economic Benefits and Job Creation
Urban farming not only addresses food security and sustainability but also creates economic opportunities for local communities. By growing and selling food locally, urban farms support local businesses and reduce reliance on imported produce. Farmers’ markets, farm-to-table restaurants, and local food cooperatives benefit from access to fresh, high-quality produce grown within the city.
Urban farming also provides jobs in urban areas, contributing to local economies and empowering residents with new skills. Farming, harvesting, managing, and distributing food all require a labor force, and urban farms often employ community members. Programs focused on youth training and job creation in urban farming are particularly impactful, as they provide young people with agricultural skills and career paths within their own communities.
Community Building and Mental Health Benefits
Beyond its environmental and economic impacts, urban farming brings people together and promotes mental well-being. Community gardens create shared spaces where neighbors can gather, work together, and connect. These spaces foster a sense of belonging and provide an opportunity for residents to work collaboratively, strengthening social bonds and building community pride.
Gardening and farming are also known to have mental health benefits. Spending time outdoors, engaging in physical activity, and nurturing plants can reduce stress, anxiety, and depression. For many city residents, urban farms and community gardens provide a much-needed green escape from the fast pace of city life, offering a sense of calm and connection to nature.
Challenges Facing Urban Farming
While urban farming has numerous benefits, it also faces challenges. Securing land in densely populated cities can be difficult, with high real estate prices making it hard for urban farms to find affordable space. Additionally, pollution from urban areas can affect soil and air quality, posing risks to crop health and requiring extra precautions.
Despite these challenges, urban farming continues to grow in popularity, with support from local governments, organizations, and individuals who see the value of bringing food production closer to home. Partnerships between cities and community groups are helping to overcome these obstacles, making urban farming a more viable option for food production in metropolitan areas.
Conclusion: Growing a Greener Future
Urban farming is transforming cities across America, offering a sustainable, community-oriented approach to food production. As more cities embrace urban farming, they are creating healthier, greener spaces that benefit residents, local economies, and the environment. By supporting urban farms and community gardens, Americans can play a role in building more resilient cities and fostering a deeper connection to the food they eat. The future of urban farming is bright, and it’s helping to grow a greener future for generations to come.
Published by: Nelly Chavez