How Are Renewable Energy Sources Transforming the Future of Energy?
Renewable energy sources are redefining how the world meets its growing energy demands. Unlike fossil fuels, renewables such as solar power, wind energy, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal energy harness natural processes to produce sustainable and clean electricity. These energy technologies are not just solutions to the global energy crisis but are vital for addressing climate change. As countries worldwide shift toward greener practices, renewable energy has become a cornerstone of this transformation.
Read Also: How Social Media Influencers and Brand Ambassadors Are Shaping the Creator Economy
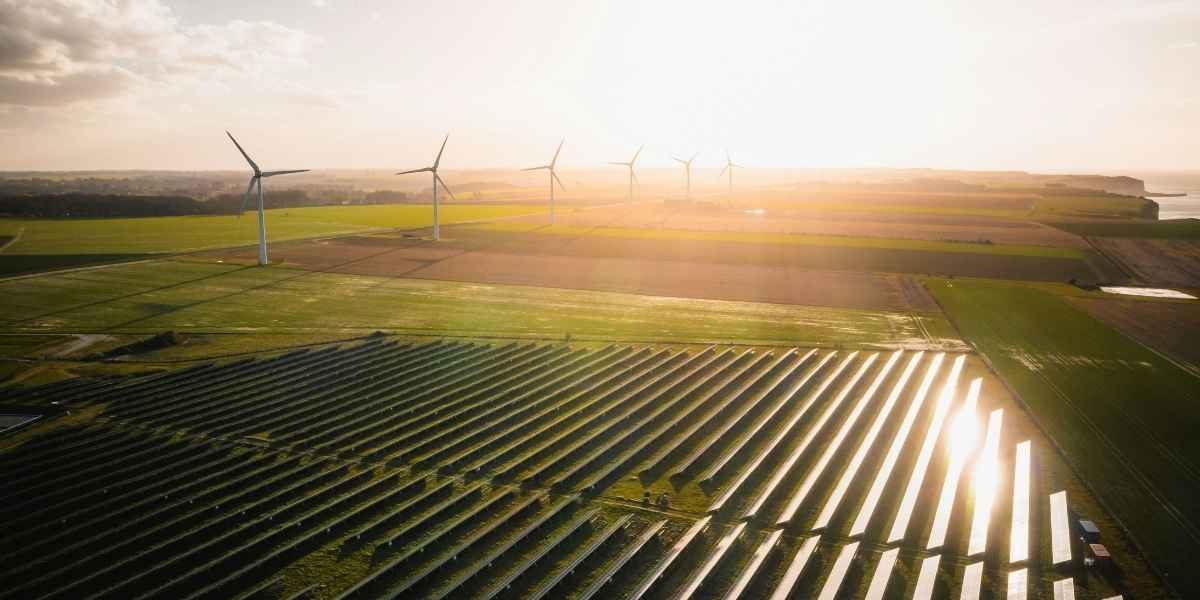
Solar energy, for example, utilizes photovoltaic cells to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. Wind energy, harnessed by turbines, is another rapidly growing source of clean power. Meanwhile, hydropower plants tap into the movement of water to generate consistent electricity, while biomass and geothermal systems provide energy by utilizing organic material and heat from beneath the Earth’s crust. These innovations are shaping a new era of sustainability and fostering resilience in energy infrastructure.
The transition to renewable energy is more than a technological shift; it represents a cultural and economic transformation. Industries are investing heavily in green technologies, and governments are creating policies to reduce carbon footprints. This dual commitment to technological progress and environmental responsibility is what makes renewable energy critical to the global fight against climate change.
What Role Does Renewable Energy Play in Combating Climate Change?
Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges facing humanity, and renewable energy holds the key to mitigating its impacts. The burning of fossil fuels, which currently dominates the global energy landscape, is responsible for the majority of greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions contribute to rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, and loss of biodiversity.
Transitioning to renewable energy reduces dependency on carbon-intensive sources. Wind and solar energy, for instance, emit little to no greenhouse gases during operation, making them essential for cutting emissions. Hydropower, which provides a reliable and stable energy source, also plays a significant role in reducing the environmental impact of energy production.
In addition to reducing emissions, renewable energy systems promote sustainability by using resources that are naturally replenished. Unlike coal, oil, or natural gas, which are finite and heavily polluting, renewables rely on abundant sources like sunlight, wind, and water. These energy technologies not only reduce harm to the environment but also support long-term energy security.
Countries adopting renewable energy have also witnessed reductions in air pollution, benefiting public health and ecosystems. For example, a significant portion of urban air pollution comes from burning fossil fuels for electricity and transportation. By replacing these with renewable options, cities can improve air quality, decrease healthcare costs, and create healthier living environments.
How Are Renewable Energy Technologies Meeting Global Energy Needs?
As global energy demands continue to rise, renewable energy technologies are proving their capability to scale and meet the needs of diverse populations. The reliability and efficiency of renewable systems have improved significantly over the past decade, making them more competitive with traditional energy sources.
Solar and wind power are leading this revolution. Solar installations now include large-scale solar farms as well as smaller, decentralized rooftop panels, which allow individuals and businesses to produce their own energy. Similarly, offshore wind farms are emerging as a game-changer, harnessing stronger and more consistent winds to generate significant amounts of electricity.
Storage technology is another critical area of innovation. Batteries, such as those used in electric vehicles or grid-scale energy storage, allow surplus energy from renewables to be stored and used when demand is high or natural conditions are less favorable. These advancements ensure that renewable systems can provide stable and reliable electricity around the clock.
Hydropower continues to provide a steady supply of energy for countries with abundant water resources, while geothermal energy offers untapped potential in regions with access to underground heat sources. Biomass, often generated from agricultural or industrial waste, provides an additional renewable option that simultaneously addresses waste management challenges.
Developing nations are also benefiting from renewable energy projects. In remote or underserved areas, renewable energy systems offer affordable and accessible power solutions. Solar-powered microgrids, for instance, provide electricity to off-grid communities, fostering economic development and improving quality of life. These advancements demonstrate that renewable energy is not only a solution for developed economies but a universal strategy for equitable progress.
Can Renewable Energy Truly Replace Fossil Fuels?
The question of whether renewable energy can entirely replace fossil fuels has fueled debates in policy, industry, and scientific circles. While the challenges are considerable, the potential for renewables to dominate global energy systems is undeniable.
One major obstacle lies in the intermittent nature of some renewable sources. Solar and wind energy depend on weather conditions, which means they are not always available when demand is highest. Investments in energy storage technologies and smart grids are crucial for overcoming these limitations. These systems enable energy to be stored and distributed efficiently, ensuring a steady power supply even during periods of low generation.
Economic factors also play a role in this transition. While the upfront cost of installing renewable energy systems can be high, their long-term benefits far outweigh these initial expenses. Over time, the decreasing cost of renewable energy technologies, combined with incentives and subsidies from governments, has made them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. The global push toward net-zero emissions is accelerating these trends, making renewable energy a viable replacement for traditional sources.
The integration of renewables into existing energy infrastructure is another challenge. Power grids, which were designed for centralized energy production, need to be adapted for decentralized renewable systems. Governments and industries are investing heavily in modernizing these grids, making them more flexible and capable of accommodating diverse energy sources.
Read Also: Maximizing Brand Reach: How Influencer Marketing Drives Success
Despite these hurdles, the global momentum toward renewable energy is undeniable. Countries like Germany, China, and India are setting ambitious targets for renewable adoption, while corporations and investors are prioritizing green technologies. These efforts underscore the widespread recognition that renewable energy is not just a part of the solution—it is the future of energy.