What Makes the North Pole So Unique?
The North Pole, a region covered in ice and snow, represents a place of extremes and mysteries. Located at the top of the world, it’s an area that has captivated explorers, scientists, and adventurers for centuries. Unlike the South Pole, the North Pole is not on a continent but instead floats on the Arctic Ocean, surrounded by shifting sea ice.
What makes the North Pole so unique isn’t just its location, but the environment that surrounds it. The area experiences polar night and polar day—months of continuous darkness in the winter and continuous sunlight in the summer. This makes the North Pole a place of extreme contrasts, both in terms of light and temperature.
Read Also: Northern USA’s Economy: Opportunities and Challenges
How Has Human Exploration Shaped Our Understanding of the North Pole?
For centuries, the North Pole was one of the last great frontiers for explorers. Early expeditions were driven by a mix of curiosity and competition. Some explorers sought to be the first to reach it, while others aimed to map the unknown region.
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, explorers like Robert Peary and Frederick Cook claimed to have reached the North Pole, though their achievements were often surrounded by controversy. It wasn’t until 1968 that an expedition on a nuclear-powered icebreaker reached the North Pole, confirming human access to this remote part of the planet.
Today, reaching the North Pole is a monumental but achievable feat for modern explorers, with icebreaker ships and expeditions making it possible for adventurers and scientists to access the area. Still, the harsh conditions and extreme cold present challenges even with modern technology.
What Impact Does Climate Change Have on the North Pole?
In recent decades, the North Pole has become a symbol of climate change. Scientists have observed significant changes in the region’s ice cover. The Arctic, including the North Pole, is warming at a faster rate than anywhere else on Earth, a phenomenon known as Arctic amplification. This accelerated warming is contributing to the melting of sea ice, which has serious implications not only for the region itself but for the global climate.
The melting ice could disrupt wildlife in the area, including polar bears, seals, and other species that rely on the sea ice for hunting and breeding. It also affects local communities and Indigenous peoples who depend on the ice-covered landscape for their traditional way of life. As sea ice melts, new shipping routes are opening, but this also leads to potential ecological harm.
What Animals Call the North Pole Home?
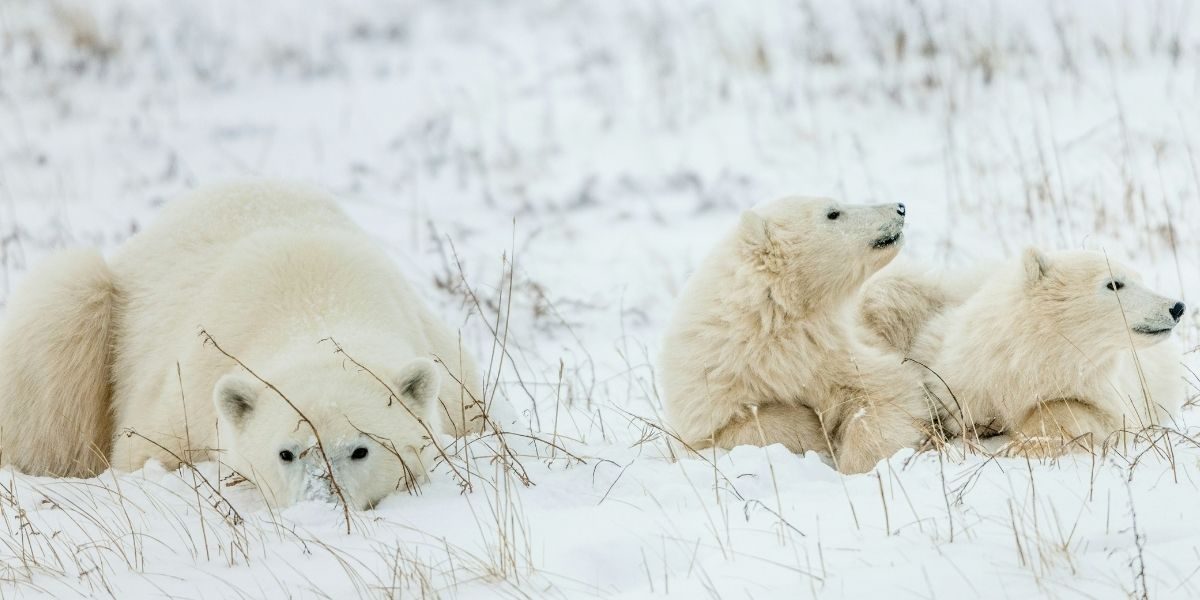
Despite its harsh conditions, the North Pole is home to an array of unique wildlife. The region’s most iconic creature is the polar bear. These powerful animals have adapted to life in the cold, with thick fur and a layer of fat to insulate them against freezing temperatures. Polar bears rely on sea ice to hunt seals, and as the ice melts, their habitats are increasingly threatened.
Seals are another significant species in the North Pole region. They use the ice to rest, raise their pups, and escape from predators. Walruses, Arctic foxes, and a variety of bird species also call this frozen landscape home.
Despite the difficult environment, life persists in this remote area, with many species adapting to the extreme conditions. However, the ongoing environmental changes threaten these delicate ecosystems, highlighting the interconnectedness of the North Pole to the planet’s broader environmental health.
How Does the North Pole Influence Global Climate?
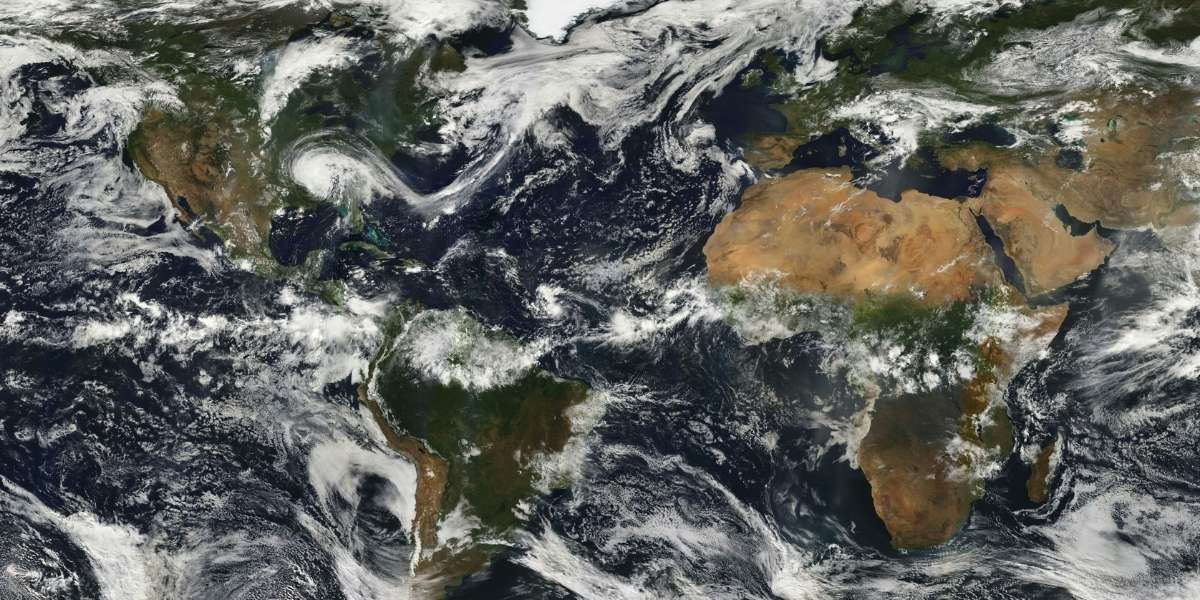
The North Pole plays a critical role in regulating the Earth’s climate. As one of the coldest regions on Earth, it helps to cool the planet. Ice reflects sunlight, helping to regulate the planet’s temperature. However, as the ice melts, more dark water is exposed, absorbing heat and contributing to further warming, creating a feedback loop.
The region also impacts weather patterns across the world. The North Pole and the surrounding Arctic influence the jet stream, which in turn affects the weather systems in the Northern Hemisphere. The melting ice and changing temperatures in the North Pole could lead to unpredictable shifts in weather patterns, affecting everything from storms to temperatures in far-off areas.
What Are the Geopolitical Implications of the North Pole?
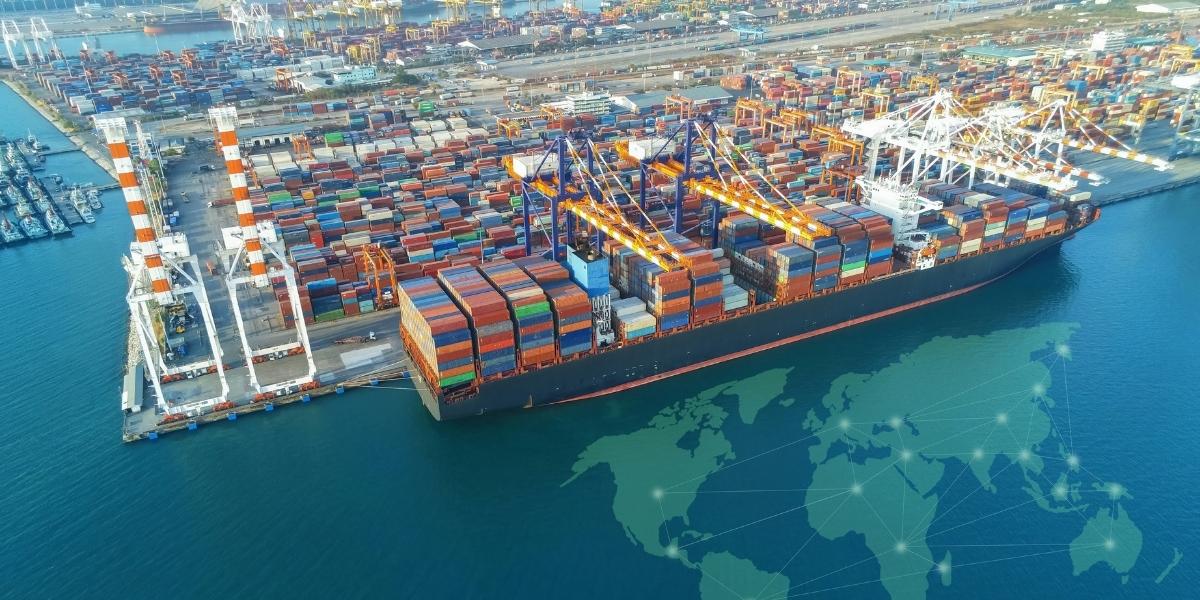
With climate change opening up new shipping routes and access to natural resources beneath the Arctic Ocean, the North Pole is becoming an area of geopolitical importance. Countries surrounding the Arctic, including Russia, Canada, and Norway, are asserting territorial claims in the region. This has led to discussions and disputes about ownership of parts of the Arctic seabed and the resources beneath it, such as oil and gas.
The growing interest in the North Pole raises questions about how to balance economic development with environmental preservation. International cooperation is essential to managing the region responsibly, ensuring that the North Pole is not only protected for future generations but that its resources are used sustainably.
Read Also: DIY Home Decor Projects to Personalize Your Living Space
What Lies Ahead for the North Pole?
Looking ahead, the future of the North Pole is uncertain. The accelerating pace of climate change and the increasing geopolitical interest in the region suggest that the coming years could be critical for its survival. The melting of ice could open new frontiers for exploration and economic development, but it could also lead to significant environmental degradation.
As scientific research continues to explore the North Pole, we may uncover more about its role in the planet’s climate system. Protecting the North Pole will require international cooperation, innovative solutions to address climate change, and a commitment to preserving its unique ecosystems.