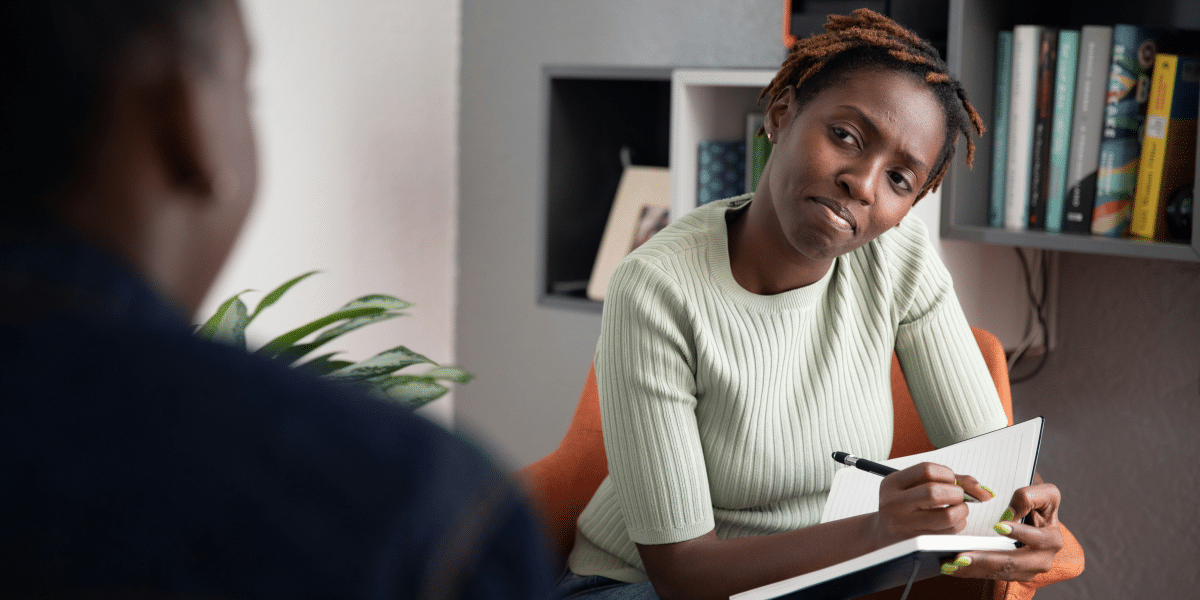
What Is Therapy?
Therapy, also called counseling or psychotherapy, is a professional service that helps individuals address mental health issues, emotional challenges, and behavioral concerns. Working with a trained therapist, individuals explore their feelings, thoughts, and behaviors, developing strategies to improve mental health and well-being.
Therapy can benefit a wide range of concerns, such as anxiety, depression, stress, trauma, relationship difficulties, and personal growth. It offers a safe, confidential space for exploring challenges and creating meaningful change.
Why Therapy Matters
Therapy plays a crucial role in mental health care and personal development. Here are some of the key reasons why therapy is important:
1. Mental Health Support
Therapy helps individuals manage conditions like anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). People can improve their mental health and quality of life by understanding symptoms and developing coping strategies.
2. Emotional Healing
Therapy offers a space to process and heal from emotional pain, trauma, and difficult experiences. It provides tools to navigate complex emotions and move forward.
3. Relationship Improvement
Therapy can enhance communication and conflict resolution skills, fostering healthier, more fulfilling relationships. Couples therapy and family therapy address issues within relationships, strengthening connections.
4. Personal Growth
Therapy encourages self-reflection and self-improvement. It helps individuals set and achieve personal goals, build self-esteem, and enhance overall well-being.
5. Stress Management
Therapy equips individuals with strategies to manage stress effectively, promoting resilience and a more balanced lifestyle.
Types of Therapy
Different therapeutic approaches cater to various needs and preferences. Here’s a brief overview of common types of therapy:
1. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors. It is effective for anxiety, depression, and other mental health concerns.
2. Psychodynamic Therapy
This therapy explores unconscious processes and past experiences to understand how they influence current behavior. It aims to increase self-awareness and emotional insight.
3. Humanistic Therapy
Humanistic therapy emphasizes personal growth and self-actualization. It focuses on the individual’s potential and encourages a positive self-view.
4. Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
DBT combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness practices. It is particularly effective for borderline personality disorder and emotional regulation.
5. Family Therapy
Family therapy involves working with family members to address issues within the family system, improve communication, and resolve conflicts.
6. Group Therapy
Group therapy brings multiple participants together under a therapist’s guidance. It offers support, shared experiences, and a sense of community.
7. Art Therapy
Art therapy uses creative processes like drawing, painting, or sculpting to help individuals express emotions and promote healing, mainly when verbal expression is challenging.
Getting Started with Therapy
Starting therapy can feel intimidating, but taking the first step is empowering. Here’s how to begin:
1. Identify Your Needs
Consider what you want to address in therapy, such as anxiety, relationship issues, or self-improvement. Identifying your needs helps you choose the right type of therapy and therapist.
2. Research Therapists
Look for licensed therapists who specialize in areas relevant to your needs. Use online directories, ask friends for referrals, or consult healthcare providers.
3. Consider Practicalities
Think about logistics, such as location, availability, and cost. Many therapists offer sliding-scale fees, accept insurance, or provide virtual sessions for added convenience.
4. Schedule a Consultation
Many therapists offer initial consultations to discuss your needs and determine whether they fit well. Use this opportunity to ask questions and gauge your comfort level.
5. Commit to the Process
Therapy requires effort and commitment. Be open to the journey, and give yourself time to explore and grow.
Benefits of Therapy
Therapy offers numerous benefits that can improve various aspects of life:
1. Emotional Support
Therapy provides a safe space to express and process emotions, reducing feelings of isolation.
2. Enhanced Coping Skills
Therapy equips you with strategies to manage stress, anxiety, and challenges more effectively.
3. Greater Self-Understanding
Therapy fosters self-awareness and personal growth by exploring thoughts, behaviors, and patterns.
4. Improved Communication
Therapy enhances communication skills, helping you express yourself clearly and resolve conflicts.
5. Increased Resilience
Therapy helps build resilience through healthier coping mechanisms and a stronger sense of self.
Maintaining Progress After Therapy
Continuing to grow after therapy is essential for long-term well-being. Here are some strategies to maintain progress:
Practice Self-Care: Prioritize activities that nurture your physical, emotional, and mental health.
Stay Connected: Surround yourself with supportive friends, family, or community groups.
Apply What You’ve Learned: Use the skills and strategies from therapy, such as mindfulness and stress management, in daily life.
Set Goals: Continue setting and working towards personal goals to stay motivated.
Periodic Check-Ins: Consider periodic sessions with your therapist to stay on track and address new challenges.
Therapy is a powerful tool for improving mental health, fostering emotional well-being, and achieving personal growth. By understanding different types of therapy, knowing how to get started, and recognizing the benefits, you can take the first step towards a healthier, more fulfilling life. Whether addressing specific mental health concerns, seeking self-improvement, or building better relationships, therapy offers the guidance and support needed for meaningful change.
Published by: Annie P.